Technology
A technology for site remediation or water treatment is selected based on feasibility studies. For sites with affected soil and groundwater, the selection criteria is generally based on United States Environmental Protection (USEPA) guidance.
Contaminants
Metals
Chromium (Cr), Hexavalent Chromium (CrVI), Selenium (Se), Arsenic (As)
Inorganic Compounds
Nitrates (NO3–), Nitrites (NO2–), Perchlorate (ClO4–)
Industrial and Remediation
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Color, Oil and Grease (O&G), Phosphorous (P), Ammonia (NH3), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), Tetrachloroethylene (PCE), Trichloroethylene (TCE), Vinyl Chloride and 1,4-Dioxane
Petroleum
Oil and Grease (O/G); Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquid (LNAPL); Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH); Methyl tert-Butyl Ether (MtBE); Benzene, Toluene, Ethyl-benzene, Xylene (BTEX)
Water Treatment | Advanced Oxidation with Ozone Peroxide
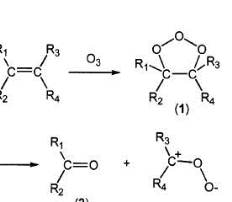 The advanced oxidation process is a proven technology for the oxidation of a wide range of compounds in water and groundwater affected with benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes (BTEX), methyl tert-butyl ether (MtBE), total petroleum hydrocarbons as gasoline (TPHg), total petroleum hydrocarbons as diesel (TPHd), tert-butyl formate (TBF), tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME), diisopropyl ether (DIPE), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), trimethylbenzene, 1,4-dioxane, trichloroethylene (TCE), perchloroethylene (PCE), 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE), 1,1-dichloroethene (1,1-DCE), vinyl chloride, and tetrahydrofuran.
The advanced oxidation process is a proven technology for the oxidation of a wide range of compounds in water and groundwater affected with benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes (BTEX), methyl tert-butyl ether (MtBE), total petroleum hydrocarbons as gasoline (TPHg), total petroleum hydrocarbons as diesel (TPHd), tert-butyl formate (TBF), tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME), diisopropyl ether (DIPE), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), trimethylbenzene, 1,4-dioxane, trichloroethylene (TCE), perchloroethylene (PCE), 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE), 1,1-dichloroethene (1,1-DCE), vinyl chloride, and tetrahydrofuran.Groundwater Remediation with Advanced Oxidation
The advanced oxidation process is a proven technology for the remediation groundwater impacted with Benzene-toluene-ethylbenzene-xylenes (BTEX), methyl tert-butyl ether (MtBE), TPH-g, tert-butyl formate (TBF), tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME), diisopropyl ether (DIPE), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), trimethylbenzene, 1,4-dioxane, trichloroethylene (TCE), perchloroethylene (PCE), 1,2-dichloroethene (1,2-DCE), 1,1-dichloroethene (1,1-DCE), vinyl chloride, and tetrahydrofuran. Continue reading



